Fingerprinting began in 1984
No-one has the same fingerprints, even our own body doesn't. Each finger can be different.
By 6 months in the womb your fingerprints are developed and shaped which will last a lifetime. They don't change. A scientist proved the validity of fingerprinting for police use by shaving his fingerprints. They grew back in the same pattern.
The three shapes categorised for identification:- Arches, loops, whorls
But more shapes are listed such as double loop, tented arch, plain loop.
I did my prints and found my thumb and forefinger are double loop and then they go into plain loop and I think my little finger in a whorl.
I also did my parents fingerprints and my Dad has a Whorl thumb print and a double loop forefinger, but the rest weren't clear. My mum's thumb is a plain loop and forefinger is a whorl with the rest unclear. Pretty fascinating if genetics play a part in the development of fingerprints. I just need to do my twin brother's.
https://www.touchngoid.com/8-common-fingerprint-patterns/
https://hastingsmuseum.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Fingerprint-Info-Activities.pdf
https://lozierinstitute.org/dive-deeper/when-and-how-fingerprints-form/
https://le.ac.uk/dna-fingerprinting/history
https://www.smithsonianmag.com/science-nature/myth-fingerprints-180971640/
https://www.crime-scene-investigator.net/fbiscienceoffingerprints.html
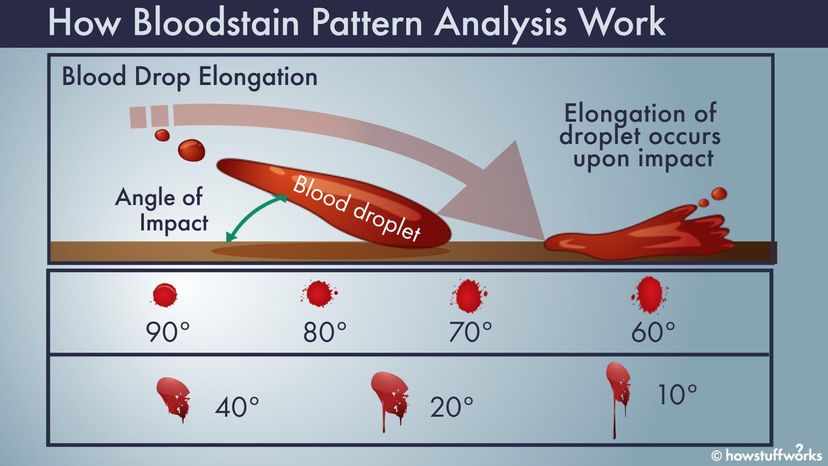
Blood Splatter Analysis.
Three basic types- Passive stain, transfer stain and projected or impact stain
Seven categories:- Passive, Projected, impact spatter, cast off, arterial gush or spurt, wipe, transfer.
Patterns of the blood spatter are determined by the velocity, direction the blood travelled, angles of impact. Spines and tails are created in the blood pattern.
https://science.howstuffworks.com/bloodstain-pattern-analysis3.htm
o+ is the most dominant and frequently occurring blood type.
DNA Evidence
Things such as Blood, Skin, Body Fluids, Hair are collected to determine a DNA profile.
Low level DNA or 'touch DNA' can be collected from places such as bruises where handled roughly.
Reference samples- biological- are used for side by side comparison.
Most DNA samples submitted to a laboratory undergo the following process:
- Extraction is the process of releasing the DNA from the cell.
- Quantitation is the process of determining how much DNA you have.
- Amplification is the process of producing multiple copies of the DNA in order to characterize it.
- Separation is the process of separating amplified DNA product to permit subsequent identification.
- Analysis & Interpretation is the process of quantitatively and qualitatively comparing DNA evidence samples to known DNA profiles.
- Quality Assurance is the process of reviewing analyst reports for technical accuracy.
| Identical Twin | 100% | N/A |
| Parent / Child Full Sibling | 50% | Varies by specific relationship |
| Grandparent / Grandchild Aunt / Uncle Niece / Nephew Half Sibling | 25% | Varies by specific relationship |
Comments
Post a Comment